express源码阅读(二)请求、中间件
一. express官方例子
var express = require("../../index");
var app = express();
app.get("/", function (req, res) {
res.send("Hello World");
});
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log("Express started on port 3000");
});分析:
app.listen做了什么?
访问/如何匹配到回调的?
二、listen
listen方法来自application.js的混入
1、express.js
混入对象到express导出的函数
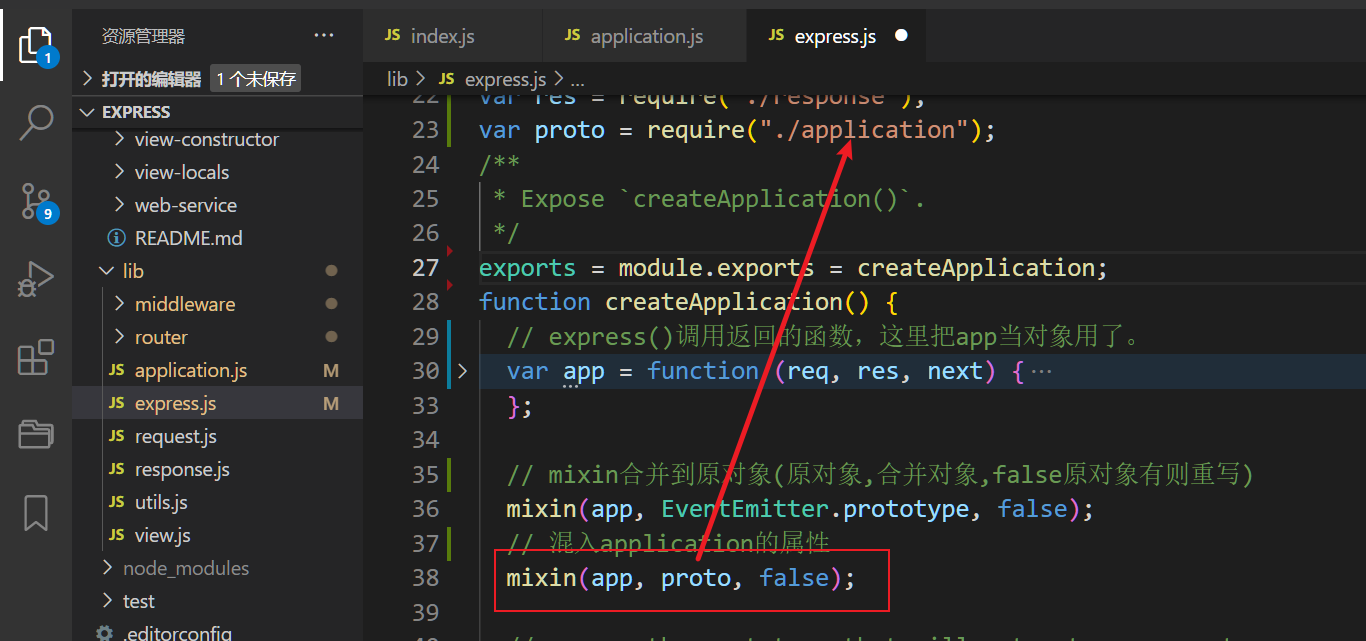
2、application.js
混入的listen方法
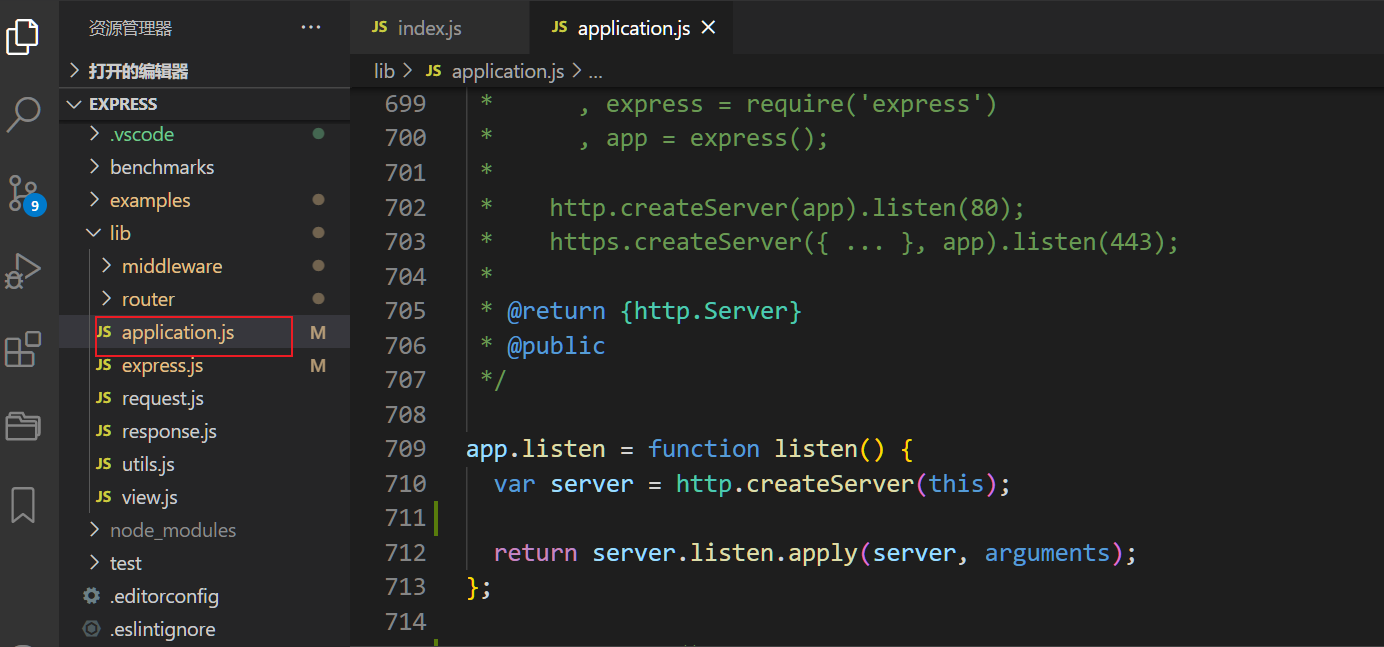
2.1 createServer
this即app函数,因为是app调用的,所以执行环境为app对象。此为this隐式绑定。
- listen函数调用
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log("Express started on port 3000");
});- listen函数执行
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res, next) {
app.handle(req, res, next);
};);
return server.listen([3000, function () {
console.log("Express started on port 3000");
}])代码执行用node的http核心模块创建服务器,监听3000端口;浏览器请求后会执行到app.handle方法,将request、response对象传递给此方法,next此时为undefined。
三、浏览器请求/
3.1 app.handle
handle方法将挂载到app中的router取出,调用router中的handle继续处理请求。
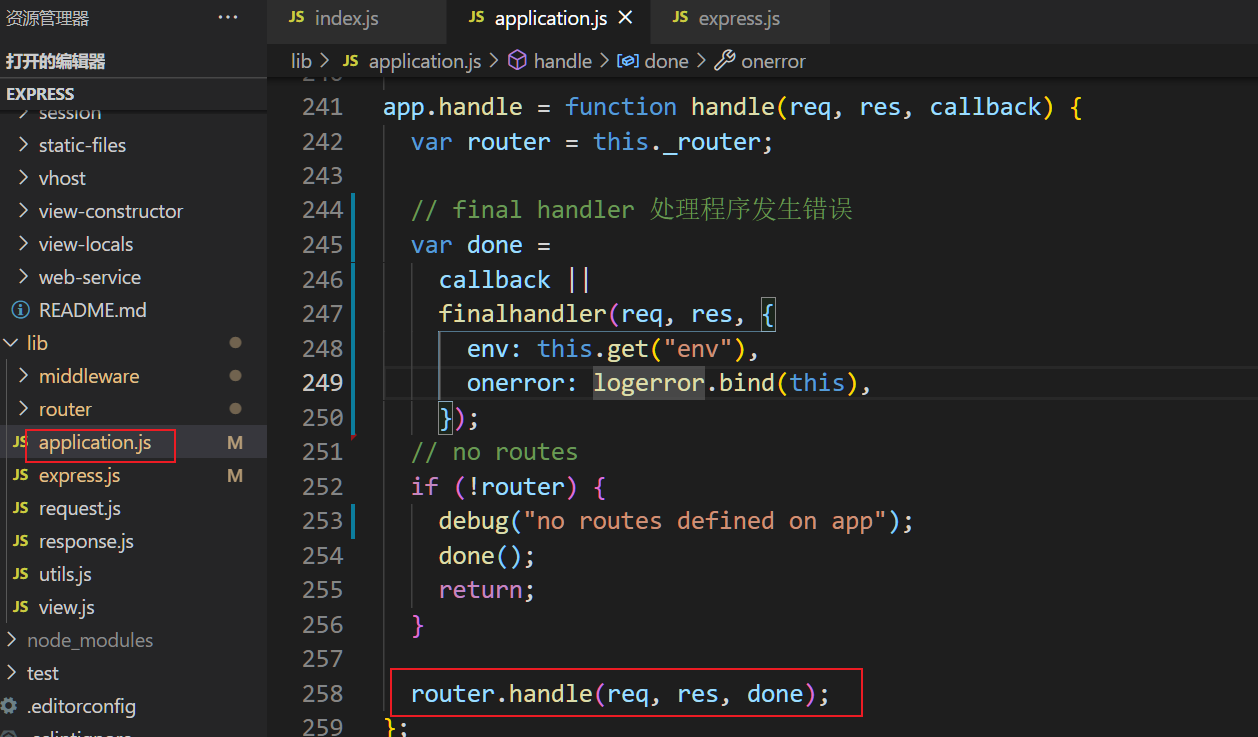
3.2 router中的handle
此方法即匹配请求真正地方,一个请求即一个中间件,根据请求路径调用next匹配中间件,最后执行中间件,再次调用next匹配下一个中间件。
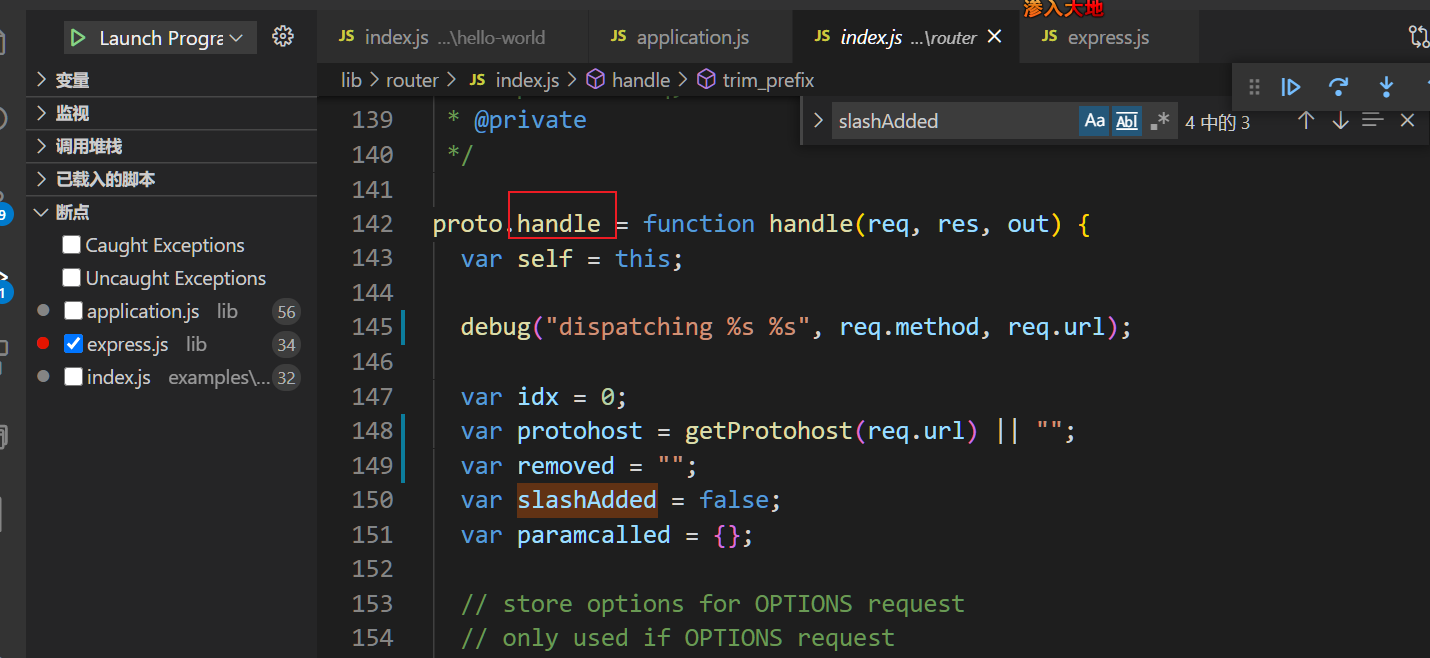
3.2.1 handle主要内容
proto.handle = function handle(req, res, out) {
var self = this;
var idx = 0;
// middleware and routes
var stack = self.stack;
next();
function next(err) {
// next("route")可以传这样传参数否则异常
var layerError = err === "route" ? null : err;
// 传参数router异常,传其他的(除route)下面代码有体现
if (layerError === "router") {
setImmediate(done, null);
return;
}
// no more matching layers
if (idx >= stack.length) {
setImmediate(done, layerError);
return;
}
// get pathname of request
var path = getPathname(req);
if (path == null) {
return done(layerError);
}
// find next matching layer
var layer;
var match;
var route;
// while匹配start
while (match !== true && idx < stack.length) {
layer = stack[idx++];
// use的中间件过来匹配为true,循环跳出,调next才会再执行找下一个匹配
match = matchLayer(layer, path);
route = layer.route;
if (match !== true) {
continue;
}
if (!route) {
// process non-route handlers normally
continue;
}
if (layerError) {
// routes do not match with a pending error
match = false;
continue;
}
var method = req.method;
// 请求方法匹配
var has_method = route._handles_method(method);
// build up automatic options response
if (!has_method && method === "OPTIONS") {
appendMethods(options, route._options());
}
// don't even bother matching route
if (!has_method && method !== "HEAD") {
match = false;
continue;
}
}
// while匹配end
// no match
if (match !== true) {
return done(layerError);
}
// store route for dispatch on change
if (route) {
req.route = route;
}
var layerPath = layer.path;
// 中间件匹配完成调用
self.process_params(layer, paramcalled, req, res, function (err) {
if (err) {
return next(layerError || err);
}
// 非全局中间件
if (route) {
return layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
}
// 全局中间件没有route
trim_prefix(layer, layerError, layerPath, path);
});
}全局中间件通过layer.keys匹配router.params
proto.process_params = function process_params(layer, called, req, res, done) {
// this即router
var params = this.params;
var keys = layer.keys;
// fast track
if (!keys || keys.length === 0) {
return done();
}
...
}router
function router(req, res, next) {}
router.params = {};3.2.2 layer.handle_request
Layer.prototype.handle_request = function handle(req, res, next) {
var fn = this.handle;
if (fn.length > 3) {
// not a standard request handler
return next();
}
try {
fn(req, res, next);
} catch (err) {
next(err);
}
};3.2.3 trim_prefix
内部核心代码
function trim_prefix(layer, layerError, layerPath, path) {
...
// 执行layer内部的中间件函数
if (layerError) {
layer.handle_error(layerError, req, res, next);
} else {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
}
}
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1