express源码阅读(一)
下载源码:https://github.com/expressjs/express
git clone https://github.com/expressjs/express.git个人总结的源码阅读方法:不要多牛逼的技术,耐心最为重要。
一、官方例子
var express = require("../../index");
var app = express();
app.get("/", function (req, res) {
res.send("Hello World");
});
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log("Express started on port 3000");
});分析:
- express函数调用做了啥?
- get方法怎么执行,如何处理路径和回调的?
- listen监听端口怎么实现的?
- 浏览器请求路径又是如何匹配的?
二、express函数调用
var express = require("../../index");
var app = express();2.1 找到require("../../index")中的导入的index.js
module.exports = require('./lib/express');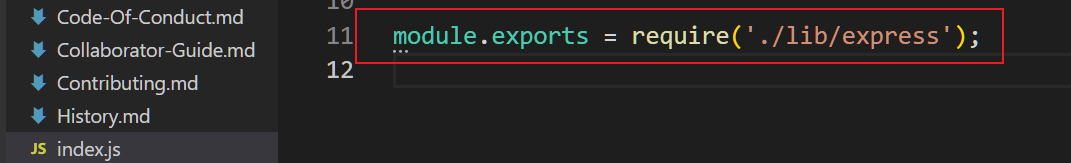
2.2 找到lib/express文件
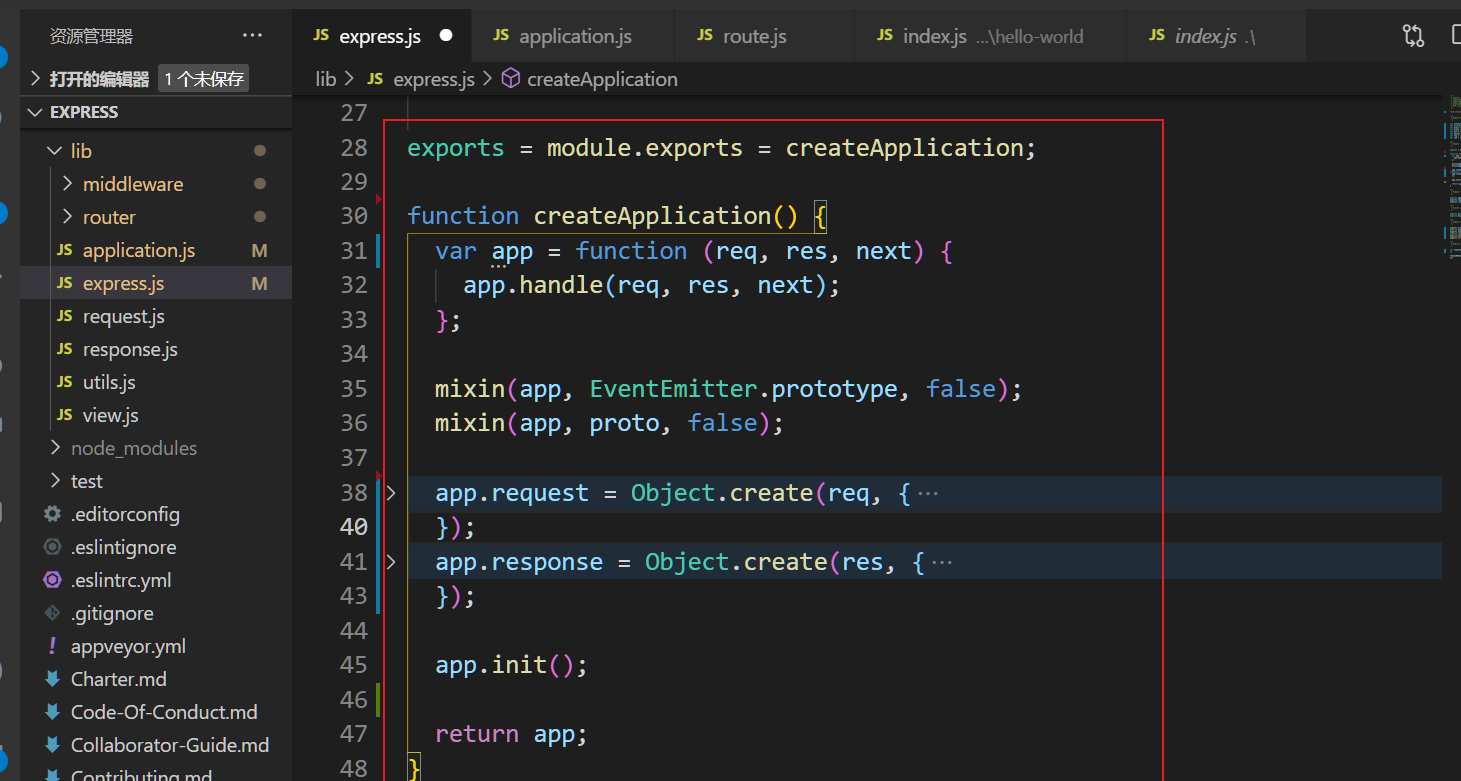
2.2.1 express中的代码解析
1. 导出模块
// 导出createApplication函数
exports = module.exports = createApplication;2. express()调用后返回的函数
var app = function (req, res, next) {
// 暂时不用关注,用户请求才走到这里
app.handle(req, res, next);
};3. mixin
合并到原对象(原对象,合并对象,false原对象有则重写)
// 使app有发布订阅的功能
mixin(app, EventEmitter.prototype, false);
// 混入application的属性
mixin(app, proto, false);EventEmitter和prote来自模块导入:
var EventEmitter = require("events").EventEmitter;
var proto = require("./application");4. 初始化配置
app.init();init方法来自proto的mixin混入,proto来自./application。
2.2.2 application.js
app.init = function init() {
this.cache = {};
this.engines = {};
this.settings = {};
this.defaultConfiguration();
};上面把app当对象用了,我写个例子说明类似情况:
function app() {}
app.usename = "修罗";
app.getUsername = function () {
console.log(this); // function app(){}
console.log(this.usename); // "修罗"
};
app.getUsername();this.defaultConfiguration();执行后给app添加了配置对象。
app.locals.settings =
app.setting = {
"x-powered-by": true,
etag: "weak",
"etag fn": function generateETag(body, encoding) {...},
env: "development",
"query parser": "extended",
"query parser fn": function parseExtendedQueryString(str) { ...},
"subdomain offset": 2,
"trust proxy": false,
"trust proxy fn": function trustNone() { return false; },
view: function View(name, options) {...},
views: "d:\\source\\express\\views",
"jsonp callback name": "callback",
};
app.mountpath = "/";三、app.get
app.get("/", function (req, res) {
res.send("Hello World");
});3.1 方法定义在application.js
application模块加载执行:
- 定义app.get、app.post等等方法
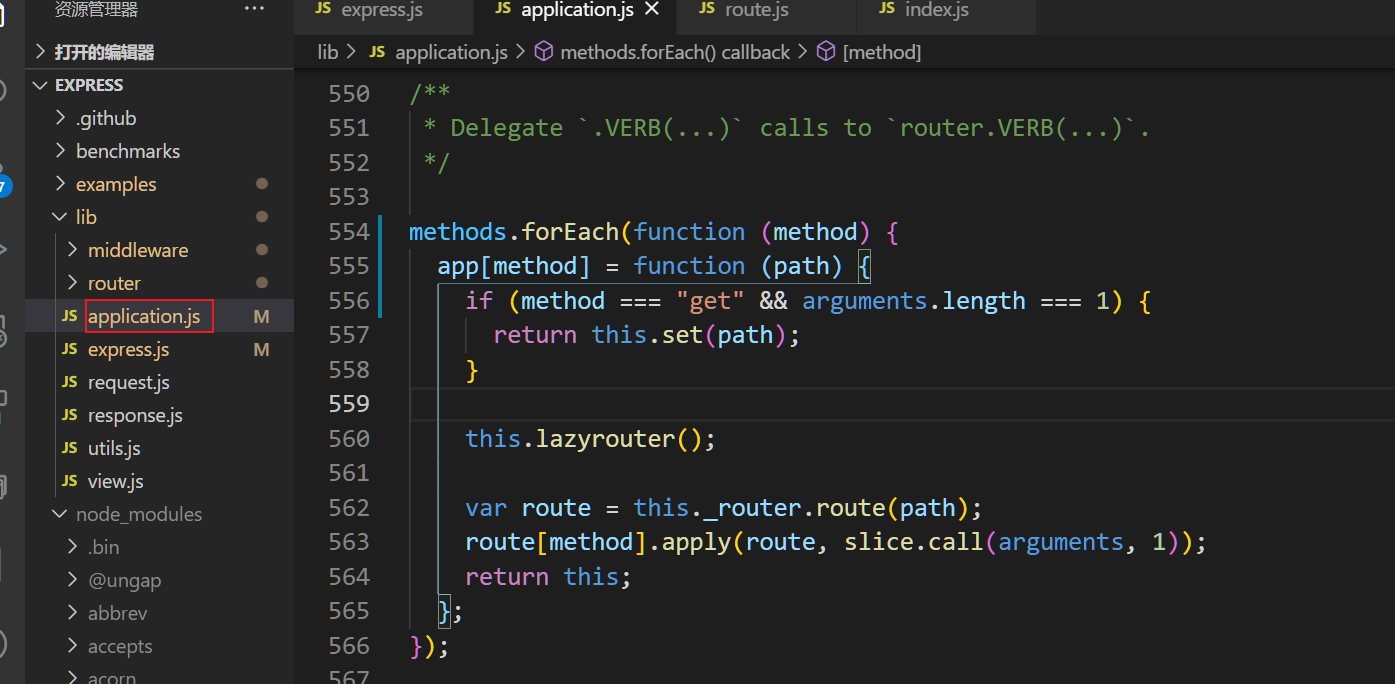
// method: [ 'get', 'post', 'put', 'head', 'delete', 'options'...]
methods.forEach(function (method) {
app[method] = function(path){...}
});3.2 例子:app.get
// 参数:"/", function (req, res) {}
app.get = function (path) {
// app.get传一个参数
if (method === "get" && arguments.length === 1) {
return this.set(path);
}
// 初始化router,只执行一次
this.lazyrouter();
// 返回route对象
var route = this._router.route(path);
// 最后调route.get(fn):只传fn,不传path过去
route.get.apply(route, slice.call(arguments, 1));
// 把app返回,链式调用
return this;
};3.3 lazyrouter
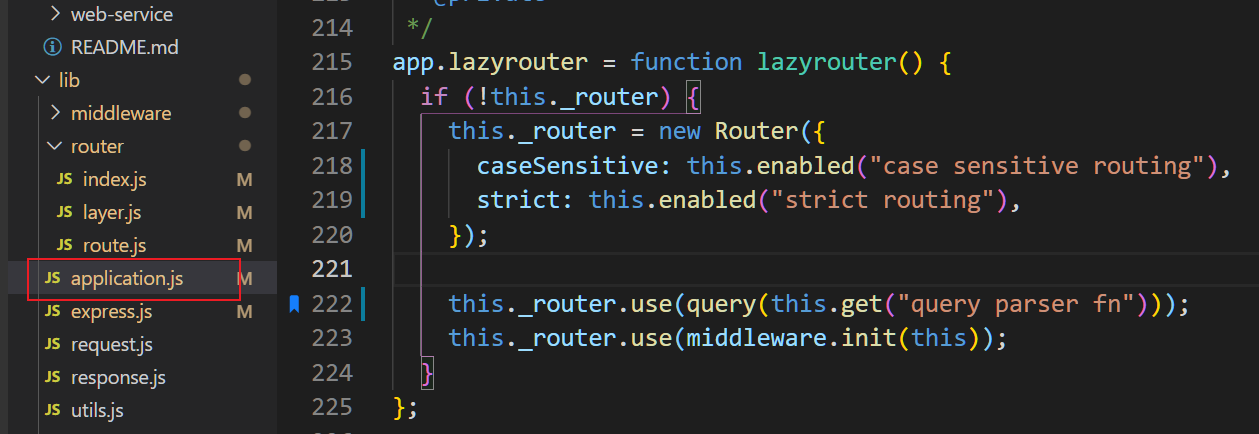
3.3.1 创建Router对象
this._router = new Router({
// 找setting中有没有,没有返回false,下面都false
caseSensitive: this.enabled("case sensitive routing"),
strict: this.enabled("strict routing"),
});- Router定义在
router/index.js
new Router即new proto()
var proto = (module.exports = function (options) {
var opts = options || {};
function router(req, res, next) {
router.handle(req, res, next);
}
// 内部函数router可以拿外部函数proto的属性
setPrototypeOf(router, proto);
router.params = {};
router._params = [];
router.caseSensitive = opts.caseSensitive;
router.mergeParams = opts.mergeParams;
router.strict = opts.strict;
router.stack = [];
// router: function(){}: { params..., __proto__: proto}
return router;
});3.3.2 router.use
this._router.use(query(this.get("query parser fn")));
this._router.use(middleware.init(this));1. this._router.use(query(this.get("query parser fn")))
this.get("query parser fn")
this.get("query parser fn") 从setting中拿到函数
(str) => qs.parse(str, { allowPrototypes: true })query()
query((str) => qs.parse(str, { allowPrototypes: true }))query函数:
返回中间件(req, res, next)=>{}函数,函数内部调了next();
// 此中间件即在req上挂了一个属性:query,url参数解析为query对象。
// 如参数:username=xiuluo&pass=hui => { usename:xiuluo, pass:hui }
module.exports = function query(options) {
...
return function query(req, res, next) {
if (!req.query) {
var val = parseUrl(req).query;
req.query = queryparse(val, opts);
}
next();
};
};this._router.use传入中间件函数
proto.use = function use(fn) {
var offset = 0;
var path = "/";
...列出本例重要代码,省略部分代码
// flatten([ fn ])
// callbacks:[(req, res, next) { next() }]
// 多维数组拍成一维数组
var callbacks = flatten(slice.call(arguments, offset));
// 遍历,每个中间件都创建了一个layer对象,并放到router的stack属性中
for (var i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) {
var fn = callbacks[i];
var layer = new Layer(
path,
{
// false,大小写不敏感
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: false,
end: false,
},
fn
);
layer.route = undefined;
this.stack.push(layer);
}
return this;
};Layer
function Layer(path, options, fn) {
// 不是通过new调用
if (!(this instanceof Layer)) {
return new Layer(path, options, fn);
}
var opts = options || {};
// 保存中间件函数
this.handle = fn;
this.name = fn.name || "<anonymous>";
this.params = undefined;
this.path = undefined;
// path的正则
// /get/: id
// pathRegexp("/get/:id").exec(/get/1) : [...] else null
this.regexp = pathRegexp(path, (this.keys = []), opts);
// set fast path flags
this.regexp.fast_star = path === "*";
this.regexp.fast_slash = path === "/" && opts.end === false;
}2.this._router.use(query(this.get("query parser fn")))
middleware.init(this)
exports.init = function (app) {
// 中间件:给请求响应对象挂一些属性
return function expressInit(req, res, next) {
// 响应头添加'x-powered-by'
if (app.enabled("x-powered-by")) res.setHeader("X-Powered-By", "Express");
req.res = res;
res.req = req;
req.next = next;
setPrototypeOf(req, app.request);
setPrototypeOf(res, app.response);
res.locals = res.locals || Object.create(null);
next();
};
};到此,lazyrouter执行完毕。
3.4 回到app.get()
// route对象挂载layer.route中
var route = this._router.route(path);
// route.get(fn):不传path过去
route[method].apply(route, slice.call(arguments, 1));router.route
这里router存layer,layer存route,route存中间件函数
function route(path) {
var route = new Route(path);
var layer = new Layer(
path,
{
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: this.strict,
end: true,
},
route.dispatch.bind(route)
);
layer.route = route;
this.stack.push(layer);
return route;
};Route
function Route(path) {
this.path = path;
this.stack = [];
// route handlers for various http methods
this.methods = {};
}route.get(fn)
route存layer
methods.forEach(function (method) {
Route.prototype[method] = function () {
var handles = flatten(slice.call(arguments));
for (var i = 0; i < handles.length; i++) {
var handle = handles[i];
var layer = Layer("/", {}, handle);
layer.method = method;
// route['method'] = true
this.methods[method] = true;
this.stack.push(layer);
}
return this;
};
});
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1