React-router及手写路由组件
资源:
React中文网:https://react.docschina.org/
react-router英文文档:https://reactrouter.com/web/guides/quick-start
react-router中文文档:http://react-router.docschina.org/
Router
1、BrowserRouter
<BrowserRouter>使用 HTML5 提供的 history API (pushState , replaceState 和 popstate 事件) 来保持 UI 和 URL 的同步。
basename: string
所有URL的base值。如果你的应用程序部署在服务器的子目录,则需要将其设置为子目录。basename 的格式是前面有一个/,尾部没有/。
<BrowserRouter basename="/kkb">
<Link to="/user" />
</BrowserRouter>上例中的Link最终将被呈现为:
<a href="/kkb/user" />2、HashRouter
<HashRouter> 使用 URL 的 hash 部分(即 window.location.hash)来保持 UI 和 URL 的同步。
basename: string
同上。
<HashRouter basename="/kkb">
<Link to="/user" />
</HashRouter>上例中的Link最终将被呈现为:
<a href="#/kkb/user" />注意:hash history 不支持 location.key 和 location.state。仍有一些边缘问题无法解决。因此任何依赖此行为的代码或插件都将无法正常使用 。
BrowserRouter与HashRouter对比
- HashRouter最简单,不需要服务器端渲染,靠浏览器的# 的来区分path就可以,BrowserRouter需要服务器端对不 同的URL返回不同的HTML,后端配置可参考:https://react-guide.github.io/react-router-cn/docs/guides/basics/Histories.html。
- BrowserRouter使用HTML5 history API( pushState, replaceState和popstate事件),让页面的UI于URL同步。
- HashRouter不支持location.key和location.state,动态路由跳转需要通过?传递参数。
- Hash history 不需要服务器任何配置就可以运行,如果你刚刚入门,那就使用它吧。但是我们不推荐在实际线上环境中用到它,因为每一个 web 应该都应该渴望使用 browserHistory。
3、MemoryRouter
把 URL 的历史记录保存在内存中的<Router>(不读取、不写入地址栏)。在测试和非浏览器环境中很有用,如React Native。
import { MemoryRouter } from 'react-routerdom';
<MemoryRouter>
<App />
</MemoryRouter>路由组件介绍
1、Link
属性 to (字符串类型)
一个字符串形式的链接地址,通过 pathname、search 和 hash 属性创建。
<Link to='/courses?sort=name' />属性 to (object 类型 )
一个对象形式的链接地址,可以具有以下任何属性
- pathname - 要链接到的路径
- search - 查询参数
- hash - URL 中的 hash,例如 #the-hash
- state - 存储到 location 中的额外状态数据
<Link to={{
pathname: '/courses',
search: '?sort=name',
hash: '#the-hash',
state: {
redirect: '/login'
}
}} />属性 replace: (bool 类型 )
当设置为 true 时,点击链接后将替换历史堆栈中的当前条目,而不是添加新条目。默认为 false。
<Link to="/courses" replace />others
你还可以传递一些其它属性,例如 title、id 或 className 等。
<Link to="/" className="nav" title="a title">About</Link>2、Redirect
属性 to (字符串类型)
要重定向到的 URL,可以是 path-to-regexp:https://www.npmjs.com/package/path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。所有要使用的 URL 参数必须由 from 提供。
<Redirect to="/somewhere/else" />属性 to (object 类型 )
要重定向到的位置,其中 pathname 可以是 path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。
<Redirect to={{
pathname: '/login',
search: '?utm=your+face',
state: {
referrer: currentLocation
}
}} />上例中的 state 对象可以在重定向到的组件中通过 this.props.location.state 进行访问。而 referrer 键 (不是特殊名称)将通过路径名 /login 指向的登录组件中的 this.props.location.state.referrer 进行访问。
3、Route
可能是 React Router 中最重要的组件,它可以帮助你理解和学习如何更好的使用 React Router。它最基本的职责是在其 path 属性与某个 location 匹配时呈现一些 UI。
Route render methods
使用 <Router> 渲染一些内容有以下三种方式:
- component
- render: func
- children: func
在不同的情况下使用不同的方式。在指定的 <Router> 中,你应该只使用其中的一种。
属性 path (字符串类型)
可以是 path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。
<Route path="/users/:id" component={User} />没有定义 path 的 <Router> 总是会被匹配。
属性 location(object 类型)
一般情况下, <Router>尝试将其 path 与当前history location(通常是当前的浏览器 URL)进行匹配。但是, 如果您需要将 <Router> 与当前历史记录位置以外的位置相匹配,则此功能非常有用
4、Router
所有 Router 组件的通用接口。通常情况下,应用程序只会使用其中一个Router:
- BrowserRouter
- HashRouter
- MemoryRouter
- NativeRouter
- StaticRouter
5、Switch
用于渲染与路径匹配的第一个子 <Router> 或<Redirect> 。
这与仅仅使用 <Router> 系列有何不同?
<Switch> 只会渲染一个路由。相反,仅仅定义一系列 <Route> 时,每一个与路径匹配的 <Route> 都将包含在渲染范围内。考虑如下代码:
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/:user" component={User} />
<Route component={NoMatch} />如果 URL 是 /about,那么 <About>、<User> 和 <NoMatch>将全部渲染,因为它们都与路径匹配。这是通过设计,允许我们以很多方式将<Route>组合成我们的应用程序,例如侧边栏和面包屑、引导标签等。
但是,有时候我们只想选择一个来呈现。例如我们在 URL 为 /about 时不想匹配 /:user(或者显示我们的 404 页面),这该怎么实现呢?以下就是如何使用 <Switch> 做到这一点:
import { Switch, Route } from 'react-router';
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/:user" component={User} />
<Route component={NoMatch} />
</Switch>现在,当我们在 /about 路径时, <Switch> 将开始寻找匹配的<Route> 。我们知道, 将<Route path="/about"/>会被正确匹配,这时<Switch> 会停止查找匹配项并立即呈现。
<Fade>
<Switch>
{/* 这里只会渲染一个子元素 */}
<Route />
<Route />
</Switch>
</Fade>
<Fade>
<Route />
<Route />
{/* 这里总是会渲染两个子元素,也有可能是空渲染,这使得转换更加麻烦 */}
</Fade>属性 location(object 类型)
用于匹配子元素而不是当前history location(通常是当前的浏览器 URL)的 location 对象。
如下例子,那这里就只匹配首页了。
<Switch location={{pathname: "/"}}>
<Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} />
<Route path="/user" component={UserPage} />
{/* <PrivateRoute path="/user" component={UserPage} /> */}
<Route path="/login" component={LoginPage} />
<Route path="/children" children={()=> <div>children</div>} />
<Route path="/render" render={() =><div>render</div>} />
<Route path="/search/:id" component={searchComponent} />
</Switch>children: node
- 所有
<Switch>的子元素都应该是<Route>或<Redirect>。只有第一个匹配当前路径的子元素将被呈现。 <Route>组件使用 path 属性进行匹配,而<Redirect>组件使用它们的 from 属性进行匹配。没有 path 属性的<Route>或者没有 from 属性的<Redirect>将始终与当前路径匹配。- 当在
<Switch>中包含<Redirect>时,你可以使用任何<Route>拥有的路径匹配属性:path、exact 和 strict。from 只是 path 的别名。 - 如果给
<Switch>提供一个 location 属性,它将覆盖匹配的子元素上的 location 属性。
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/users" component={Users} />
<Redirect from="/accounts" to="/users" />
<Route component={NoMatch} />
</Switch>实现
目录
RouterContext
传递BrowserRouter的内容
BrowserRouter
import React, { Component } from "react";
// react-router-dom的库
import { createBrowserHistory } from "history";
import { RouterContext } from "./RouterContext";
export class BrowserRouter extends Component {
// 拼接match,保证switch有初始值,同时可以在router匹配404页面(没写path的route)
static computeRootMatch(pathname) {
return {
path: "/",
url: "/",
params: {},
isExact: pathname === "/",
};
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// history可以拿到当前路由,跳转路由...,并且兼容性强
this.history = createBrowserHistory();
this.state = {
location: this.history.location,
};
// 监听路由切换
this.unlisten = this.history.listen((location) => {
// 设置state,后面传递给子组件
this.setState({ location });
});
}
// 组件卸载解除监听
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.unlisten) {
this.unlisten();
}
}
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Provider
value={{
history: this.history,
location: this.state.location,
match: BrowserRouter.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname),
}}
>
{this.props.children}
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}
}Link
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./RouterContext";
export default class Link extends Component {
handleClick = (event, history) => {
event.preventDefault();
history.push(this.props.to);
};
render() {
const { to, children } = this.props;
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => (
<a
href={to}
onClick={(event) => this.handleClick(event, context.history)}
>
{children}
</a>
)}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}Route
简化版
加强版
import React, { Component, Children } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./RouterContext";
import matchPath from "./matchPath";
export default class Route extends Component {
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
const {
path,
computedMatch,
children,
component,
render,
} = this.props;
// const match = context.location.pathname === path;
const location = this.props.location || context.location;
// matchPath对path的拼接转对象操作,match优先从props拿
const match = computedMatch
? computedMatch
: path
? matchPath(location.pathname, this.props)
: context.match;
const props = {
...context,
location,
match,
};
// children, component, render 能接收到(history, location match),
// 所以我们定义在props,传下去
// match 渲染children, component, render 或者null
// match的时候如果children存在:function或者children本身
// 不match children 或者 null
// children是和匹配无关
/**
* match?(
* // children存在的情况
* children ? (typeof children === 'function' ? children(props): children)
* // children不存在的情况,判断component,component不存在判断render,最后都不存在为null
* :(component ? (React.createElement(component,props)) : (render ? render(props) : null)
*
* ):(typeof children === 'function' ? children(props):null)
*/
return (
<RouterContext.Provider value={props}>
{match
? children
? typeof children === "function"
? children(props)
: children
: component
? React.createElement(component, props)
: render
? render(props)
: null
: typeof children === "function"
? // 这里的children不管是否匹配match都可以存在,这里能不能直接返回,就不判断了?
// match匹配: children是function或者是节点
// 不match:不匹配,只有children是function才执行匹配
children(props)
: null}
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}switch
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./RouterContext";
import matchPath from "./matchPath";
export default class Switch extends Component {
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
// 优先用props上的location
const location = this.props.location || context.location;
// 找出渲染的,第一个符合匹配的元素,存在element
let element,
match = null;
let { children } = this.props;
// children里都是匹配的Route
React.Children.forEach(children, (child) => {
// match为空表示还没匹配,并且合法
if (match === null && React.isValidElement(child)) {
element = child;
// child的path是否存在
const path = child.props.path;
match = path
? // 返回一个对象
matchPath(location.pathname, {
...child.props,
path,
})
: // 上一级帮我们存的
context.match;
}
});
return match
? React.cloneElement(element, {
location,
computedMatch: match,
})
: null;
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}Redirect
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./RouterContext";
export default class Redirect extends Component {
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
const { history } = context;
const { to } = this.props;
// history.push(location)
// 跳转到to
return <LifeCycle onMount={() => history.replace(to)} />;
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}
class LifeCycle extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
if (this.props.onMount) {
this.props.onMount.call(this, this);
}
}
render() {
return null;
}
}测试代码:
app.js
导入
路由
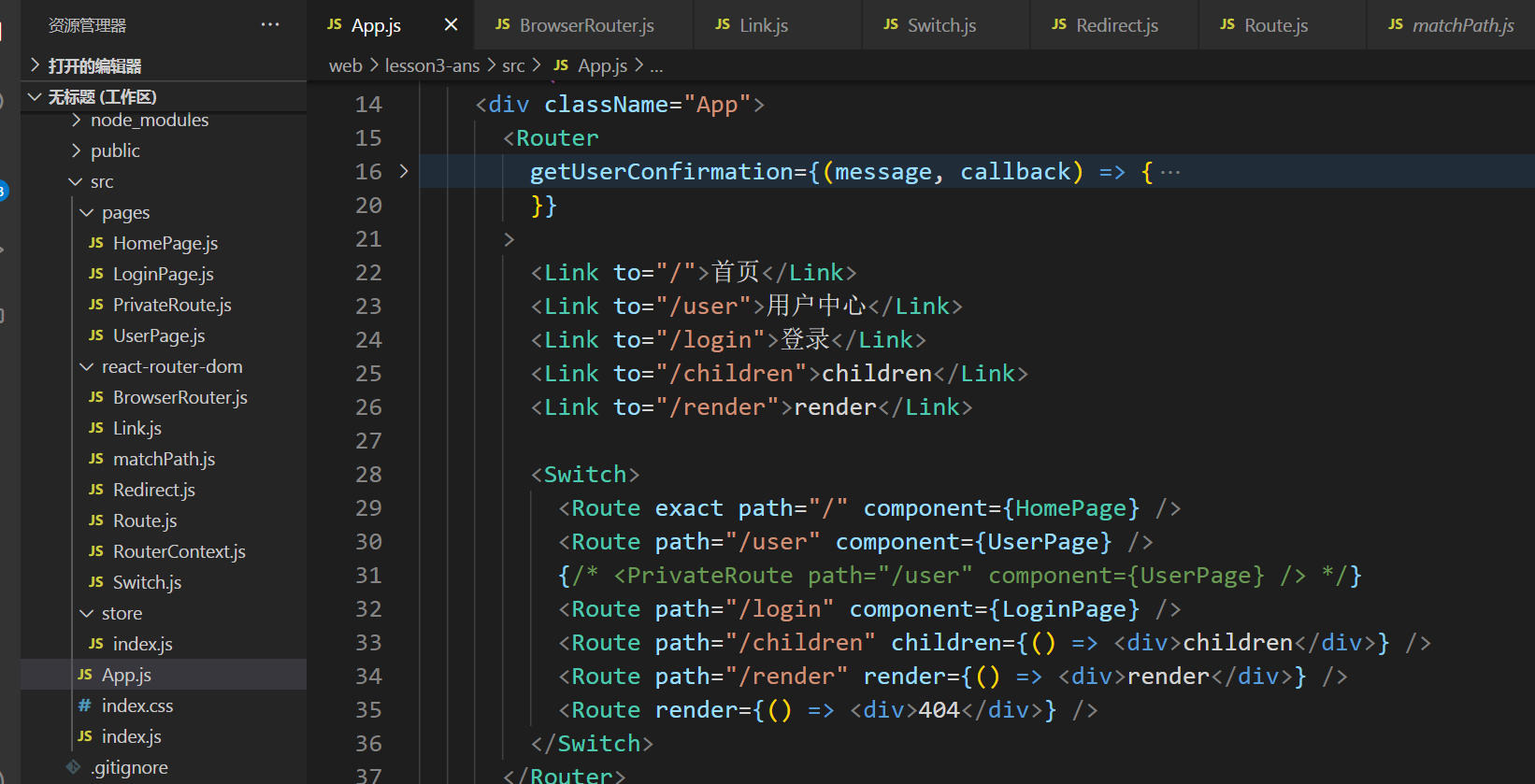
页面
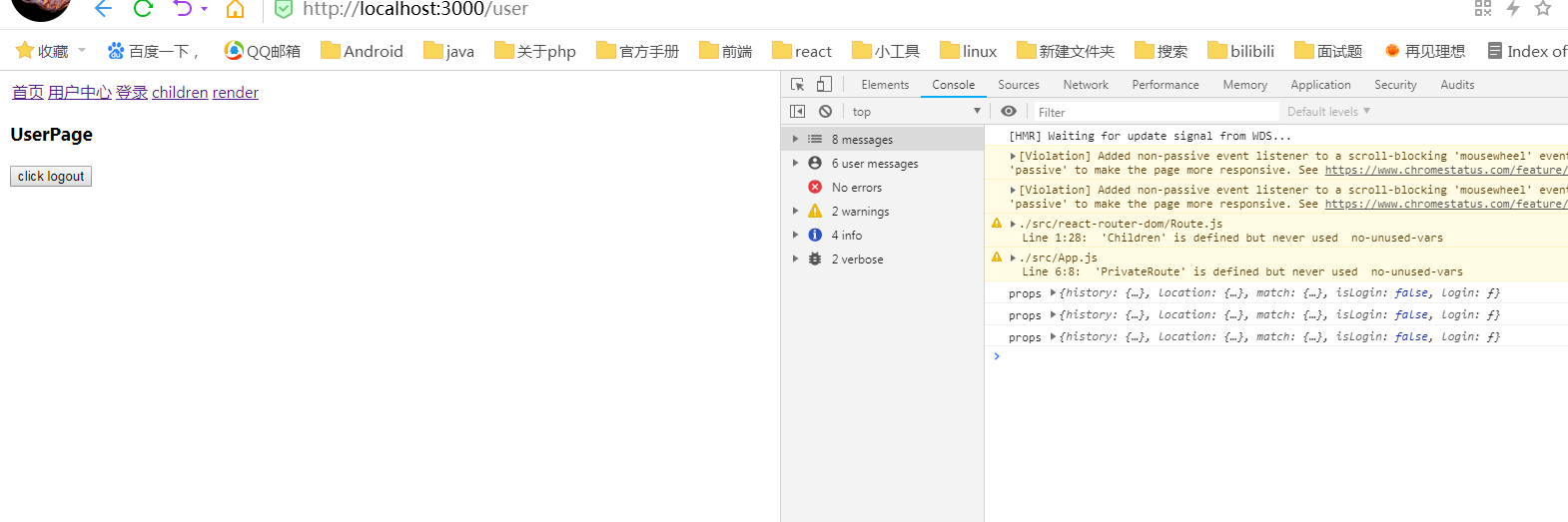
附录:matchPath.js
import pathToRegexp from "path-to-regexp";
const cache = {};
const cacheLimit = 10000;
let cacheCount = 0;
function compilePath(path, options) {
const cacheKey = `${options.end}${options.strict}${options.sensitive}`;
const pathCache = cache[cacheKey] || (cache[cacheKey] = {});
if (pathCache[path]) return pathCache[path];
const keys = [];
const regexp = pathToRegexp(path, keys, options);
const result = { regexp, keys };
if (cacheCount < cacheLimit) {
pathCache[path] = result;
cacheCount++;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Public API for matching a URL pathname to a path.
*/
function matchPath(pathname, options = {}) {
if (typeof options === "string" || Array.isArray(options)) {
options = { path: options };
}
const { path, exact = false, strict = false, sensitive = false } = options;
const paths = [].concat(path);
return paths.reduce((matched, path) => {
if (!path && path !== "") return null;
if (matched) return matched;
const { regexp, keys } = compilePath(path, {
end: exact,
strict,
sensitive
});
const match = regexp.exec(pathname);
if (!match) return null;
const [url, ...values] = match;
const isExact = pathname === url;
if (exact && !isExact) return null;
return {
path, // the path used to match
url: path === "/" && url === "" ? "/" : url, // the matched portion of the URL
isExact, // whether or not we matched exactly
params: keys.reduce((memo, key, index) => {
memo[key.name] = values[index];
return memo;
}, {})
};
}, null);
}
export default matchPath;

1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1